Vba last used row in Excel
As the name implies, this chapter is going to explain about determining the last used row in a sheet.
So, What's is use of this simple calculation? Why should one care about how many rows have been used?
To answer the questions, consider a simple case, where we have a spreadsheet, say, daily sales data, and is updated on daily basis.
So after a month, 30 rows would have been completed and the next day, the data added should be at the 31st row.
When it is done programatically, it does not know the exact number of days, the data is present.
So there must be some logic, where the program should input the data immdiately after the last used row,
This is where, this logic comes to help.
The Syntax:
- Sheets(
).Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Rows
Confusing?? Let us break the code into small parts
- Rows.Count
This simply returns the integer 65K, which is the maximum value an Integer can hold.
- .End(xlUp).Row
This is the main logic. Here, Excel traverses from Row 65K along Column A until it finds a non-empty value.
the first occurrence of a non-empty value is the last used row from the top.
The following example illustrates this;
- Sub lastrow()
- Dim lrow As Integer
- lrow = Sheets("Q33").Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
- MsgBox lrow
- End Sub
Before running the above code, just check the last used row in this sheet.
The program should return that row number.
The Screenshot of the Editor is as shown below:
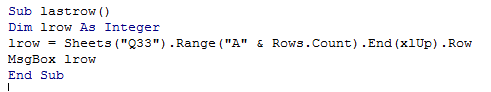
Note that, only the text I the cells are considered while finding the last used row and not any images.
For example, the above example would return 30 if these two lines are not present.